Jump To: Support > KB > NetManager > Webserver > htaccess
Controlling access to the NetManager webserver
Important Concepts
Do not confuse file access (as you would get by mapping a drive to the webspace internally) with web access (access from anywhere using a webbrowser).
Do not confuse websites which include their own login mechanism (where you enter details into a webpage and then submit) with standard web-authentication (where your browser will present a standard pop-up login box).
If users are asked to log in, they will log into a chosen realm. The realm is the word or phrase you see in the login box. Once you have logged into a given realm, you will not be asked to login again to access all web-resources on the same server with the same realm. The realm in the examples below is "NetManager webfile access". Therefore, if you want single-sign-on, you must use the same realm.
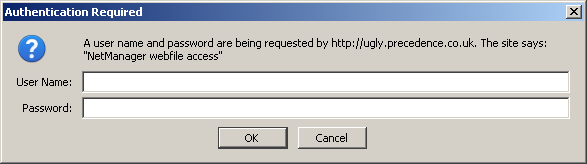
Firefox login window
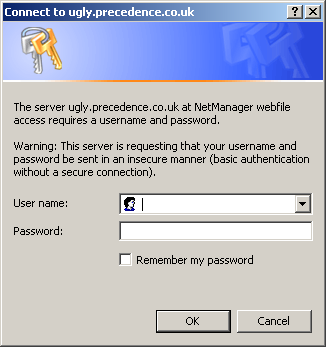
Internet Explorer login window
How it works
Per-directory settings, including access rights, are set in a .htaccess file in the target directory. All child directories will inherit settings from their parents unless overridden with another .htaccess file.
Creating a .htaccess file
You could read the Apache documentation, but the NetManager provides a simpler method: the mkhtaccess command.
To use the mkhtaccess command, go to a Command Line. The syntax is simple; like most commands you can use the -h option to view basic help:
netmanager 1# mkhtaccess -h
Syntax: mkhtaccess [-haq] [-g group] [-r realm] <dir>
-h = this message
-g = allow access to given group(s) - can specify multiple times
-r = set authentication realm (default: NetManager Intranet)
-a = always prompt for user/pass even on internal network
(default is either internal network or valid password)
-q = run quietly
<dir> is the directory to create the .htaccess file in
At its simplest, you can just type mkhtaccess with no options and no directory specified. This will create a .htaccess in the root of the webarea with the following properties:
- Realm is NetManager Intranet
- Access from internal networks (or, more explicitly, network ranges configured as Trusted) will be given access without having to log on
- All users attempting to access externally will have to log on, any valid username and password will be allowed
netmanager 2# mkhtaccess Access to 'www' will be allowed from internal networks without having to logon. From externally, anyone with a valid username and password will have access
This behaviour can be easily modified:
- Using the -a flag will not grant access to internal networks, i.e. you will always have to log on
- Using the -r flag allows you to set the realm (you will need to put quotes around the realm if it contains spaces)
- The -q flag will stop the command summarising what has been done
- You can grant access to only certain groups by using the -g flag. You can use the -g flag multiple times if you want to give access to more than one group
- You can give a directory name to operate in. If this does not begin with a /, it will be relative to the root of the webspace
Example usage
Open access to internal networks, password-protected externally with a custom realm:
netmanager 3# mkhtaccess -r "Our School Intranet" Access to 'www' will be allowed from internal networks without having to logon. From externally, anyone with a valid username and password will have access
Configure a staff-only subfolder (called staffonly) to always require a username and password even for internal users and to grant access to only the 'teaching' and 'nonteaching' groups:
netmanager 4# mkhtaccess -r "Our School Intranet" -g teaching -g nonteaching -a staffonly All users, both internally and externally, will need to logon to access 'staffonly' Only the following groups will be allowed access: teaching nonteaching