SSL-AD
Jump To: Support > KB > NetManager > SSL > AD
Enabling LDAPS on Active Directory
- Firstly, you must configure your own local certificate authority
- Determine the fully qualified domain name of your domain controller(s). This example uses
DC.internal.precedence.co.uk - Create a text file using Notepad on your domain controller. It should contain the following. Note the Subject line needs to be altered to include the full domain name of the domain controller in question:
[Version]
Signature="$Windows NT$
[NewRequest]
Subject = "CN=DC.internal.precedence.co.uk" ; Alter this to your FQDN
KeySpec = 1
KeyLength = 2048
; Can be 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, or 16384.
; Larger key sizes are more secure, but have
; a greater impact on performance.
Exportable = TRUE
MachineKeySet = TRUE
SMIME = False
PrivateKeyArchive = FALSE
UserProtected = FALSE
UseExistingKeySet = FALSE
ProviderName = "Microsoft RSA SChannel Cryptographic Provider"
ProviderType = 12
RequestType = PKCS10
KeyUsage = 0xa0
[EnhancedKeyUsageExtension]
OID=1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1 ; this is for Server Authentication - Save the file as
C:\cert.inf - At a Windows command prompt, change to the root folder (
cd \) and typecertreq -new cert.inf request.csr:
- Open a web-browser and go to webadmin. Navigate to the Security > Certificates section
- Click on the Certificate Authority tab
- Click on Download in the Certificate: section to download the CA cert (filename will be ca.crt)
- In the Sign Certificate section, click Browse (or Choose File depending on your browser) and locate
C:\request.csr. Click on Issue certificate from CSR - The certificate will be issued and visible in the Issued certs section:
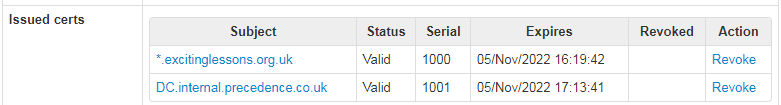
- Click on its name to download the certificate to
C:\. The filename will be based on the certificate subject, to make it easier to import you may change its name if you wish. - To make Windows trust certificate from your local CA, go to a Windows command prompt and type
certutil -addstore "Root" C:\ca.crt: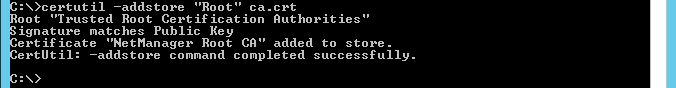
- You may then import your signed certificate with
certreq -accept <certificate file name>. N.B. You must do this after adding the CA cert to the trust store or this step will fail:
- Reboot your domain controller for the change to take effect
- To test LDAPS, run the
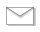
ldpcommand on the domain controller - Pick Connect... from the Connection menu
- Enter the fully-qualified name of your domain controller, enter 636 as the port number and tick the SSL box. Click OK:
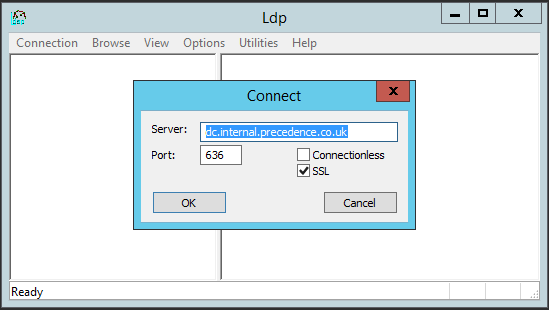
- If you don't get a Cannot open connection error, then LDAPS is working.
- You can test further by picking Bind... from the Connection menu and logging as the current user: