Jump To: Support > KB > NetManager > Network > Routing
Routing
Routing determines how network traffic travels through your network and beyond. At its simplest, the destination IP address is compared against a list of known networks and the traffic is sent out on the appropriate network interface. If there is not rule covering how to get to the destination, it will sent to the default gateway.
For directly connected networks, this is quite simple. For example, if interface A has IP address 10.1.1.1 with a netmask of 255.255.255.0 and interface B has address 10.2.1.1 with a netmask of 255.255.255.0, then to reach a computer with IP 10.1.1.2 interface A is used and to reach 10.2.1.2 interface B is used. For any other IP addresses, the default gateway will be used and that can be left to make any onwards decisions.
Sometimes you may have another network which is not directly connected, but which is reachable by using one of your internal networks (e.g. if you have VLANs via a core switch). In this situations, you need to set up a static route that says To reach this range of IP addresses, you need to go via here. To configure static routes use Network > Routing in Webadmin.
In the following example, we can see a static route for the 192.168.10.0/255.255.255.0 network reachable via 192.168.1.254: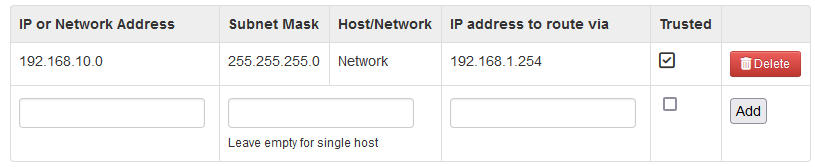
If you have very complex needs (e.g. only web traffic should be sent via a specific route), you may need to use Policy-Based Routing in the firewall.