Jump To: Support > KB > IBM > SAN > BatteryWarning
Expiration of SAN Controller Batteries
N.B. newer SAN firmware (07.35.41.00 or later) alters how the battery state is determined. Please read Determining battery state section below
Overview
Like any high-performance RAID controller, the controllers in IBM SANs have a RAM-based write-cache. This allows data to be held in fast RAM before being written to the slower discs and so stops the servers attached to the SAN being held up by disc seeks, etc. Like RAM in a computer, if the power is lost the data held in it will be lost. If this happened, major corruption could occur on the discs as the servers would assume the data was safely on the permanent disc storage. Therefore, the controllers have battery backups that will maintain the data in the RAM for a period of time if the power is lost.
If the batteries fail, the controllers will disable the RAM write-cache leading to a large drop in performance of the SAN. The batteries have a designed lifespan of around 2 years.
By default, the SAN will test the batteries every 3 months. This involves a complete discharge and recharge, during which the write-cache is disabled (i.e. performance will be impacted) for several hours. For this reason, the so-called learning cycle would not want to be run any more frequently.
Determining battery state
N.B. Battery state monitoring is much improved with newer SAN firmware (full documentation here). With firmware of 07.35.41.00 or later, Smart Battery Learn Cycle tracks the actual performance of the batteries and only warns when the battery is no longer able to maintain the up time requirement of 72 hours. If you receive a Defective Battery warning, this warns of imminent failure and the battery should be replaced ASAP.
To determine your firmware version, open the Storage Subsystem Profile window and scroll down: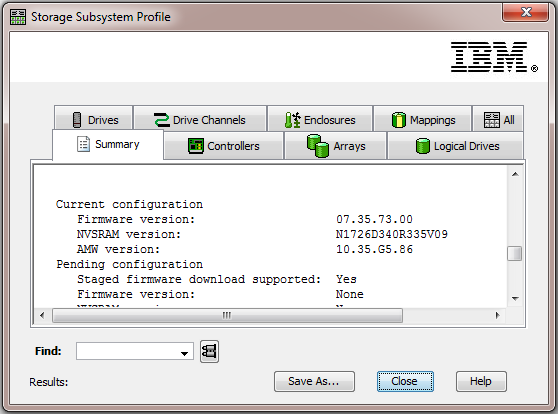
If your firmware is older than 07.35.41.00, the SAN simply uses a clock which may be reset (as the real age of the battery is not known by the SAN). It will give warnings when they approach 720 days old.
When a new battery is fitted, you must reset its clock back to zero to remove any warnings. It will apparent that you could, of course, reset this counter at any stage even without replacing a battery to remove any warnings. This will clear the warning light on front of the SAN meaning that if any other warnings or errors are found they will not be hidden by the battery warning, but you should be aware that that battery or batteries are, of course, living on borrowed time.
The batteries will not immediately fail when they reach 720 days, but once that is exceeded, they have reached the end of their designed life. It would therefore be prudent to take steps to prepare for unexpected battery failure as if a battery does fail, performance will be significantly impacted until a replacement is sourced.
Therefore, Precedence recommends that your SAN is upgraded to the latest firmware. Alternatively, when the batteries approach 720 days old and the initial warnings are displayed, you should source replacement batteries'''. Once received, you may either fit them straight away for your peace of mind in the knowledge that there will be no unexpected performance penalties or you may keep them close by ready for when the current batteries finally do fail.
Warnings
The warning light of an IBM SAN will come on for various warning events, including these battery related events:
- Event 2113 – cache battery nearing expiration
- Event 210C – cache battery failed
These events can be confirmed using the IBM DS Storage Manager software.
Q&A
Should you reset the battery age?
If battery age tracking is enabled, you need to reset the age of your battery if the Recovery Guru process tells you to do so or when you replace the battery.
What happens if you do not replace the battery once it has failed?
If you do not replace the battery in the controller, the controller cannot complete write caching. Data will not be cached in the event of a power loss.
How is the battery tested?
Batteries are routinely tested using learn cycles. The learn cycle completes these operations:
- Discharges the battery to a pre-determined threshold
- Charges the battery back to full capacity
It might take several hours for a learn cycle to complete. Write caching on all logical drives is disabled during this time. Learn cycles are scheduled to start automatically at regular intervals, at the same time and on the same day of the week. The interval between cycles is described in weeks. It is possible to adjust the interval.
For mission-critical data storage, Precedence Technologies' recommendation is to purchase replacements for both batteries once Event 2113 (cache battery nearing expiration) has been noted. Past this point, optimal operation of batteries cannot be guaranteed although the SAN may continue to operate as normal for some time. Prolonged use of old batteries increases the chances of data loss in the event of a power failure. By the time a further warning event has been noted the batteries may have degraded to the point where they cannot maintain a charge. This advice is reflected in the recovery steps offered by the Recovery Guru:
- Replace the battery now and assume the risk of losing cached data.
- Replace the battery during your next scheduled downtime (maintenance period).
- Wait until the battery reaches its expiration date before you replace it.
Procedure for battery replacement when using a dual controllers SAN
- If there are any hosts connected to this storage subsystem that are NOT running a host-based, multi-path failover driver, stop I/O to the storage subsystem from each of these hosts.
- Place the affected controller offline.
- From the Support tab, click the Manage Controllers link, and then click the Place Controller Online or Offline link.
- Select the affected controller, then select Place controller offline.
- Click the OK button.
- Click the Save As button in the Recovery Guru dialog to save the remaining steps to a file. These steps may no longer be accessible from the Recovery Guru dialog after you complete step 4.
- Click the Recheck button to rerun the Recovery Guru. There should be an Offline Controller problem reported in the Summary area.
- Follow the Offline Controller Recovery Steps, until you have removed the controller. After you have removed the controller, do not continue with the Offline Controller Recovery steps until you are instructed to do so later in this procedure.
- Replace affected battery with a new replacement battery. Refer to your hardware documentation for the battery replacement procedure.
- Complete the remaining Offline Controller Recovery Steps. Once you have completed the Offline Controller Recovery Steps, go to step 8.
- Record the installation date (today's date) and the new replacement date (according to the battery's warranty).
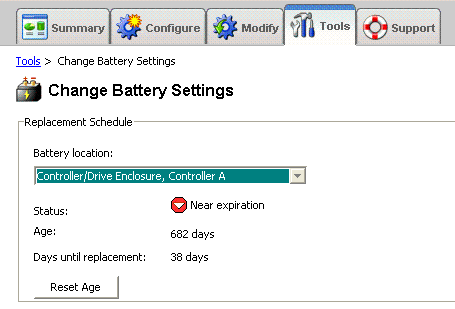
- From the Tools tab, click the Change Battery Settings link.
- Select the battery you just replaced, and then click Reset to set the affected battery's age to zero.
Notes: The time it takes to fully charge the battery depends on the model of the battery and its current state. While it is charging, the battery will report a Charging status. Consult the appropriate hardware manual for your model. If the battery is SBD-capable (the Smart battery field in the Details area is YES), then the battery will also start an initial Learn Cycle once the battery is fully charged. Write caching will be reinstated once the initial Learn Cycle is complete.
Click the Recheck button to rerun the Recovery Guru. The failure should no longer appear in the Summary area. If the failure appears again, contact your technical support representative.